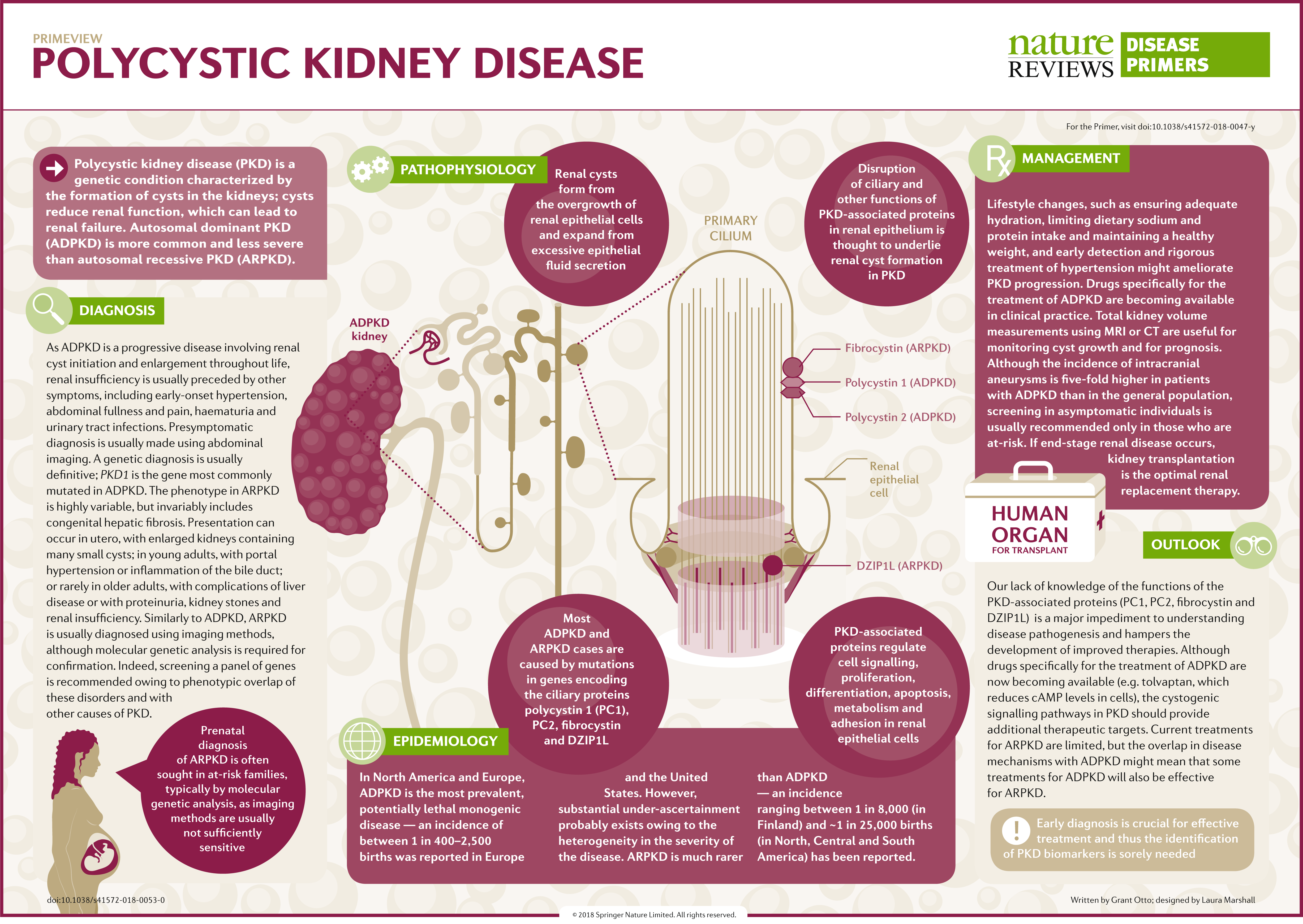
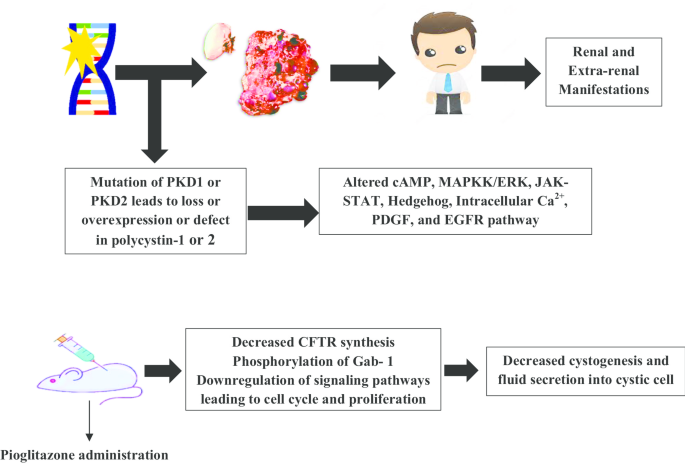
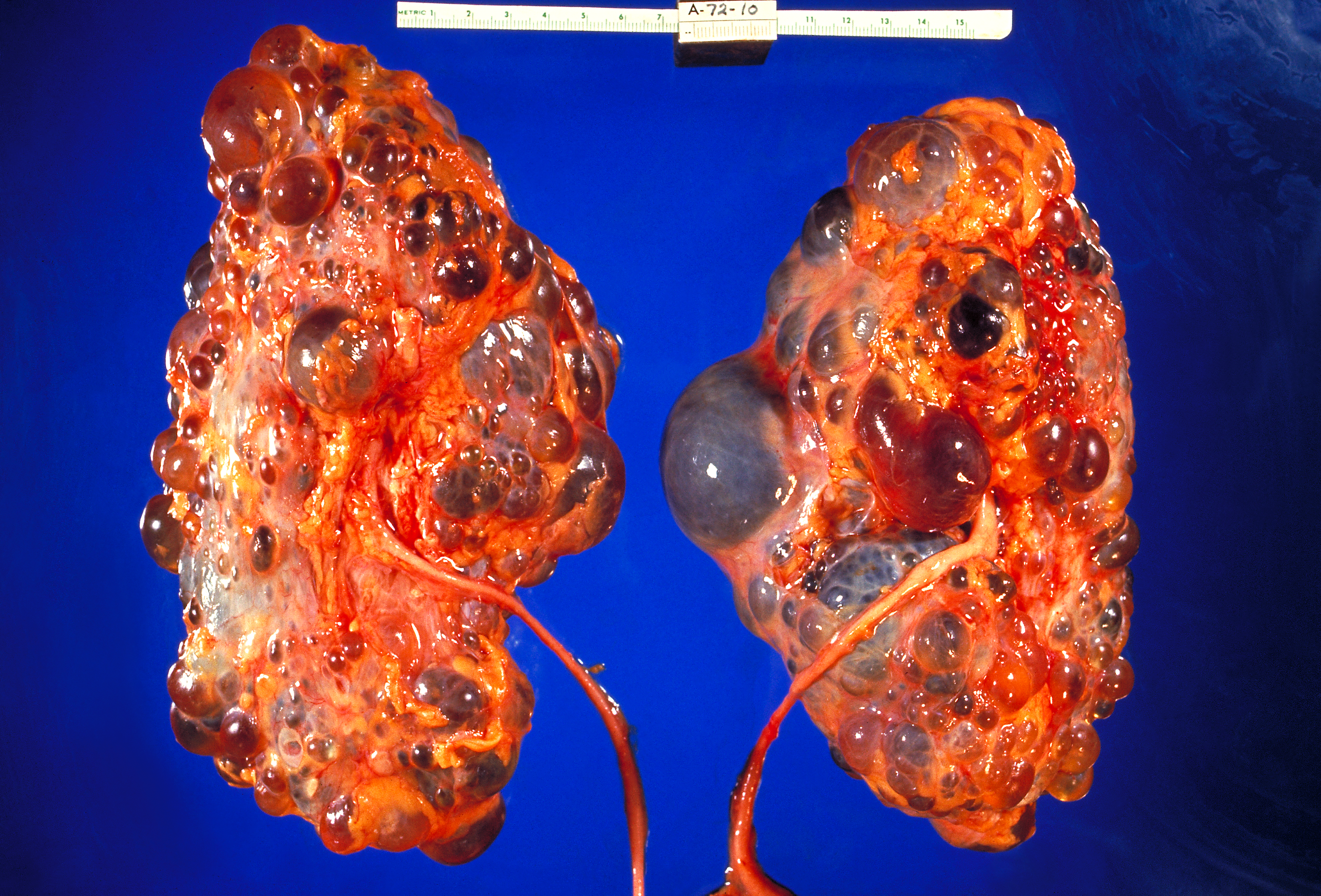
Polycystic Kidney Disease Research
Polycystic kidney disease research. PKHD1 is the gene that is responsible for the vast majority of ARPKD. However some cases have been related to a new gene that was recently identified DZIP1L gene as well as several ciliary genes that. Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is considered the most common life-threatening monogenic inherited disease.
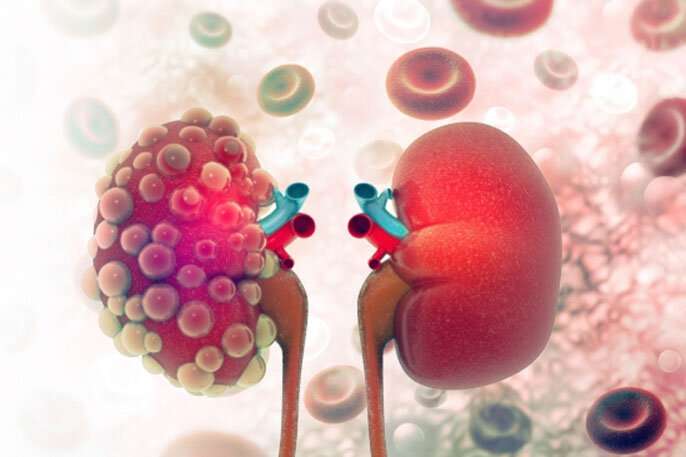
Renal tubular epithelial cells in human adult polycystic kidney disease ADPKD are characterized by increased proliferative activity leading to cyst growth with less cellular differentiation. The most common form autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is a disorder most often diagnosed in adults and caused by mutation in PKD1 or PKD2. The aim of this study was to evaluate the possibility of different BKV replication patterns in patients with polycystic kidney disease versus non-ADPKD patients.
Polycystic Kidney Disease Research and Translation Centers PKD Centers support research in cilia-related diseases and foster basic and clinical research to discover ways of combatting cystic diseases of the kidney in adults and children. The autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease proteins are thought to have a sensory role on cilia within tubules. The purpose of our research is to understand how mutations of PKD genes cause polycystic kidney disease.
This leads to renal enlargement distortion of the normal structure. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is one of the most common potentially lethal monogenic diseases and is caused predominantly by mutations in polycystic kidney disease 1 PKD1 and PKD2 which encode polycystin 1 PC1 and PC2 respectively. And polycystic kidney disease PKD were created simultaneously by a research group on progressive kidney disorders led by Seiichi Matsuo funded by the Ministry of Health Labour and Welfares research project for.
Research has shown a link between various forms of polycystic kidney disease and primary cilia which are sensory organelles that protrude from the apical surface of epithelial cells. Research into polycystic kidney disease PKD is an active area of research both for scientists like Dr Jill Norman who study the genetics and disease at the microscopic and molecular level and for doctors who conduct clinical trials. Testing new compounds in animal models of polycystic kidney disease.
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is a common genetic disorder characterized by bilateral renal cyst formation. Recently the role of noncoding RNAs in particular microRNAs has been described in polycystic kidney diseases. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease ADPKD is a devastating genetic disorder that causes numerous cysts in the kidneys and remains a leading cause of renal failure.
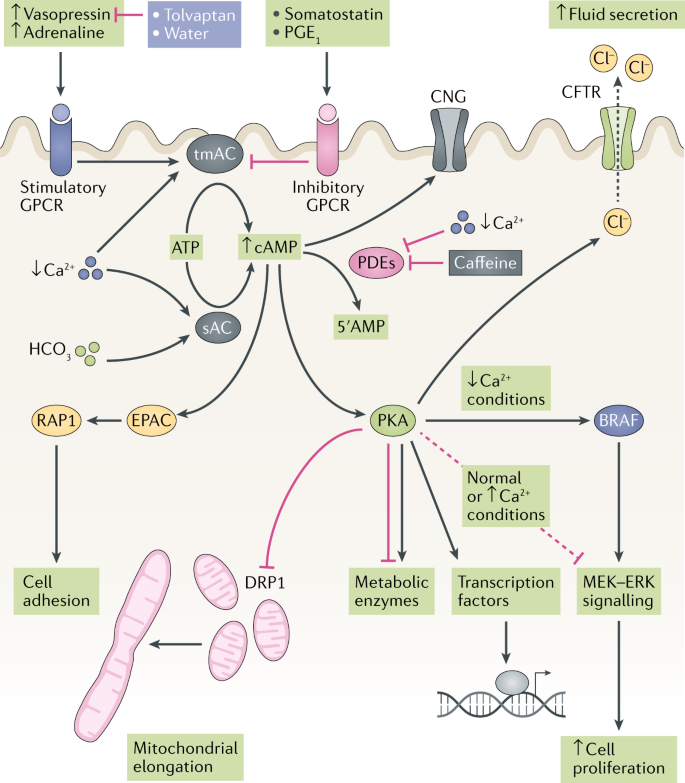
Mayo research has shown that a new drug tolvaptan can dramatically slow the development and progression of polycystic kidney disease in animal models. However the only FDA-approved therapy for ADPKD tolvaptan is limited to slowing-down disease progression and has associated side effects.
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is considered the most common life-threatening monogenic inherited disease.
In the past 20 years of studies of polycystic kidney disease Dr. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is one of the most common potentially lethal monogenic diseases and is caused predominantly by mutations in polycystic kidney disease 1 PKD1 and PKD2 which encode polycystin 1 PC1 and PC2 respectively. ADPKD affects over 600000 people in the US alone and millions worldwide. During disease progression kidney tubule epithelial cells proliferate to form fluid-filled cysts that eventually. The autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease proteins are thought to have a sensory role on cilia within tubules. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is a common genetic disorder characterized by bilateral renal cyst formation. The purpose of our research is to understand how mutations of PKD genes cause polycystic kidney disease. However the only FDA-approved therapy for ADPKD tolvaptan is limited to slowing-down disease progression and has associated side effects. Mayo research has shown that a new drug tolvaptan can dramatically slow the development and progression of polycystic kidney disease in animal models.
Recently the role of noncoding RNAs in particular microRNAs has been described in polycystic kidney diseases. ADPKD affects over 600000 people in the US alone and millions worldwide. PKD is one of the most common serious mendelian disorders of man and causes 4-5 percent of all end stage kidney disease in the United States. In the past 20 years of studies of polycystic kidney disease Dr. Recently the role of noncoding RNAs in particular microRNAs has been described in polycystic kidney diseases. We have learnt much about blood pressure control and the use of drugs to reduce kidney and liver cysts. Mayo research has shown that a new drug tolvaptan can dramatically slow the development and progression of polycystic kidney disease in animal models.





































Post a Comment for "Polycystic Kidney Disease Research"