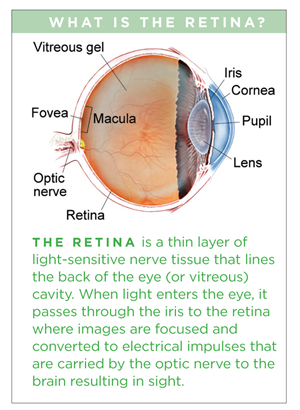
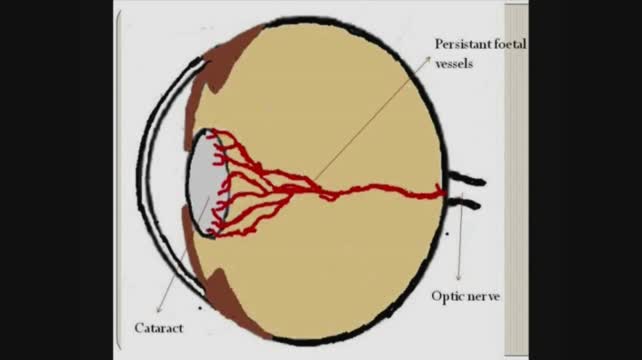
Persistent Fetal Vasculature Syndrome
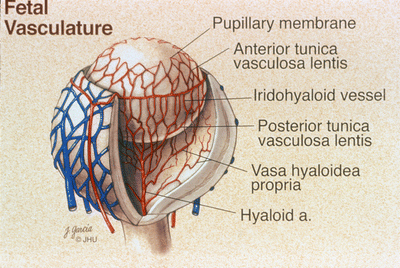
Persistent fetal vasculature syndrome. PHACE Syndrome is a neurocutaneous disease spectrum encompassing the following features. Posterior fossa brain malformations large facial Hemangiomas Arterial anomalies Coarctation of the aorta and cardiac defects and Eye abnormalities. Persistent fetal vasculature and persistent fetal vasculature syndrome are names that identify a condition that used to be called persistent hyperplasia of the primary vitreous or PHPV.
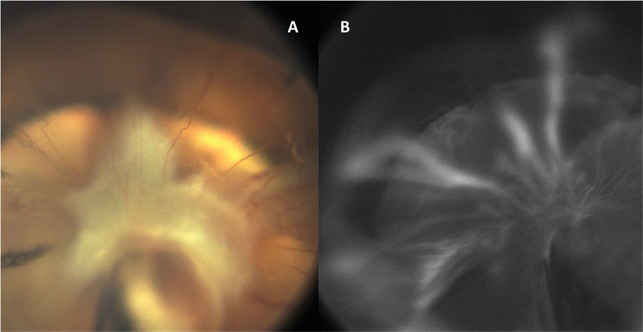
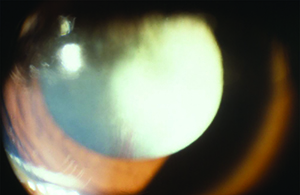
In some eyes the stalk of persistent fetal vessels may not opacify the visual axis of the lens the part light rays pass through the. Lenticonus persistent fetal vasculature and coloboma of the right eye with morning glory disc anomaly and falciform retinal folds of the left eye. It is a condition that has to do with the way the eyes developed before the.
Suggestion of recognition of this syndrome PHPVB as well as persistent fetal vasculature syndrome PFVS should be implemented diagnostics towards other optic and systemic development defects. These vessels are persistent and not newly developed and therefore are best referred to as rubeosis iridis. Persistent Fetal Vasculature Syndrome It is a congenital ocular disorder where fetal vasculature persists.
Nevertheless some cases of autosomal dominant and autosomal. It can be either subtle no disturbance in vision or severe profound visual loss. Microcornea posterior megalolenticonus persistent fetal vasculature chorioretinal coloboma MPPC syndrome.
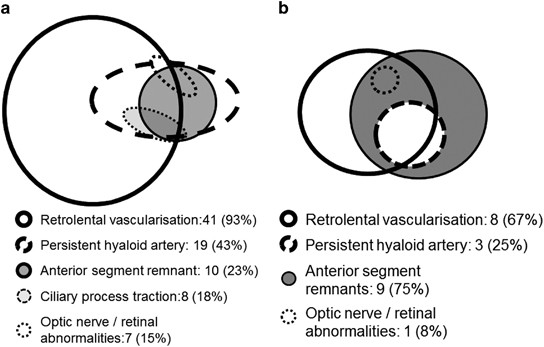
This set of findings does not tell the examiner whether retinal dysplasia is present or not. Case series post vitrectomy Patients with microcornea PFV chorioretinal coloboma and microphthalmos can benefit from surgical intervention when functional decline or. This condition arises from failure of the hyaloid vasculature to undergo normal programmed involution.
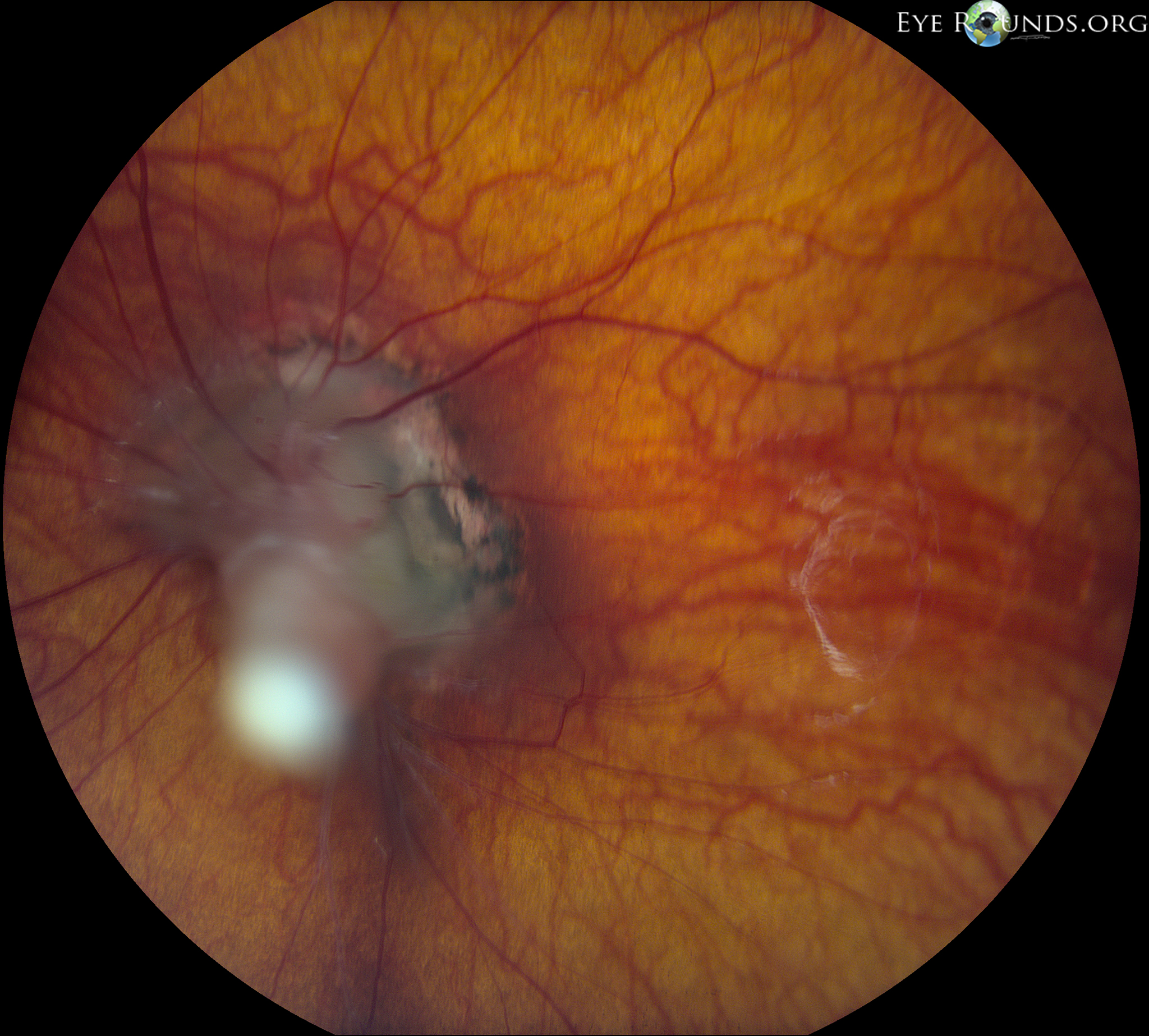
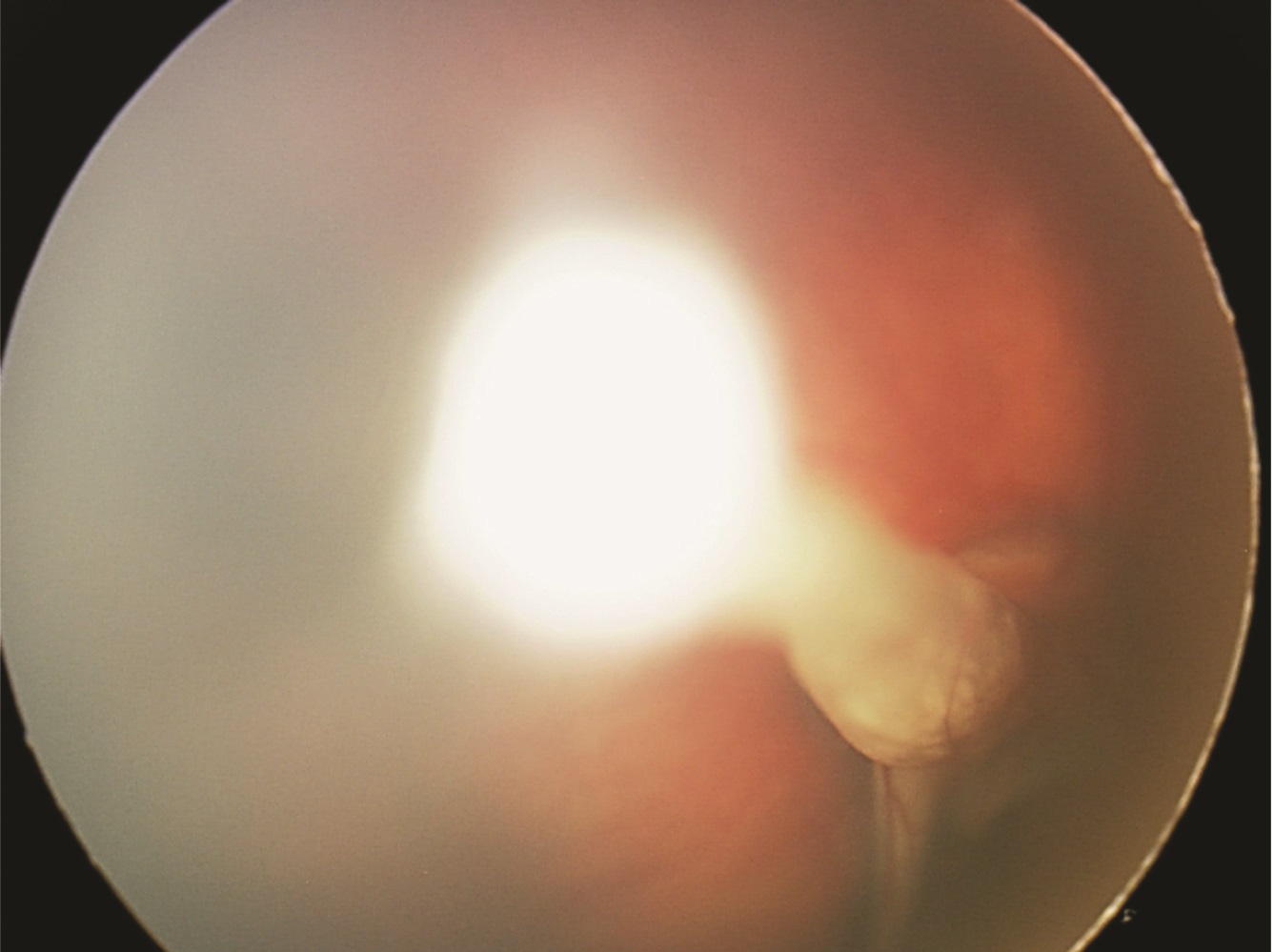
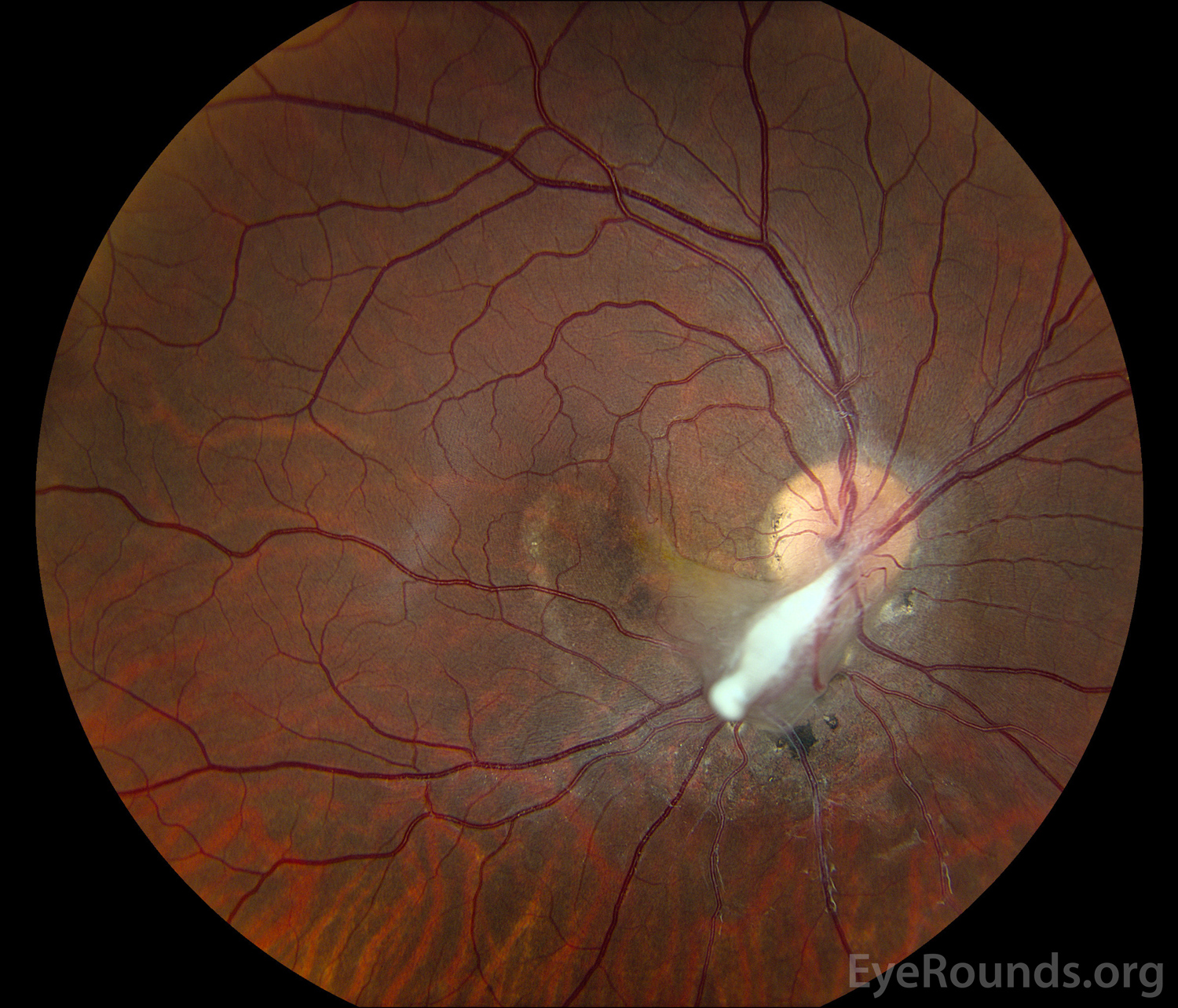
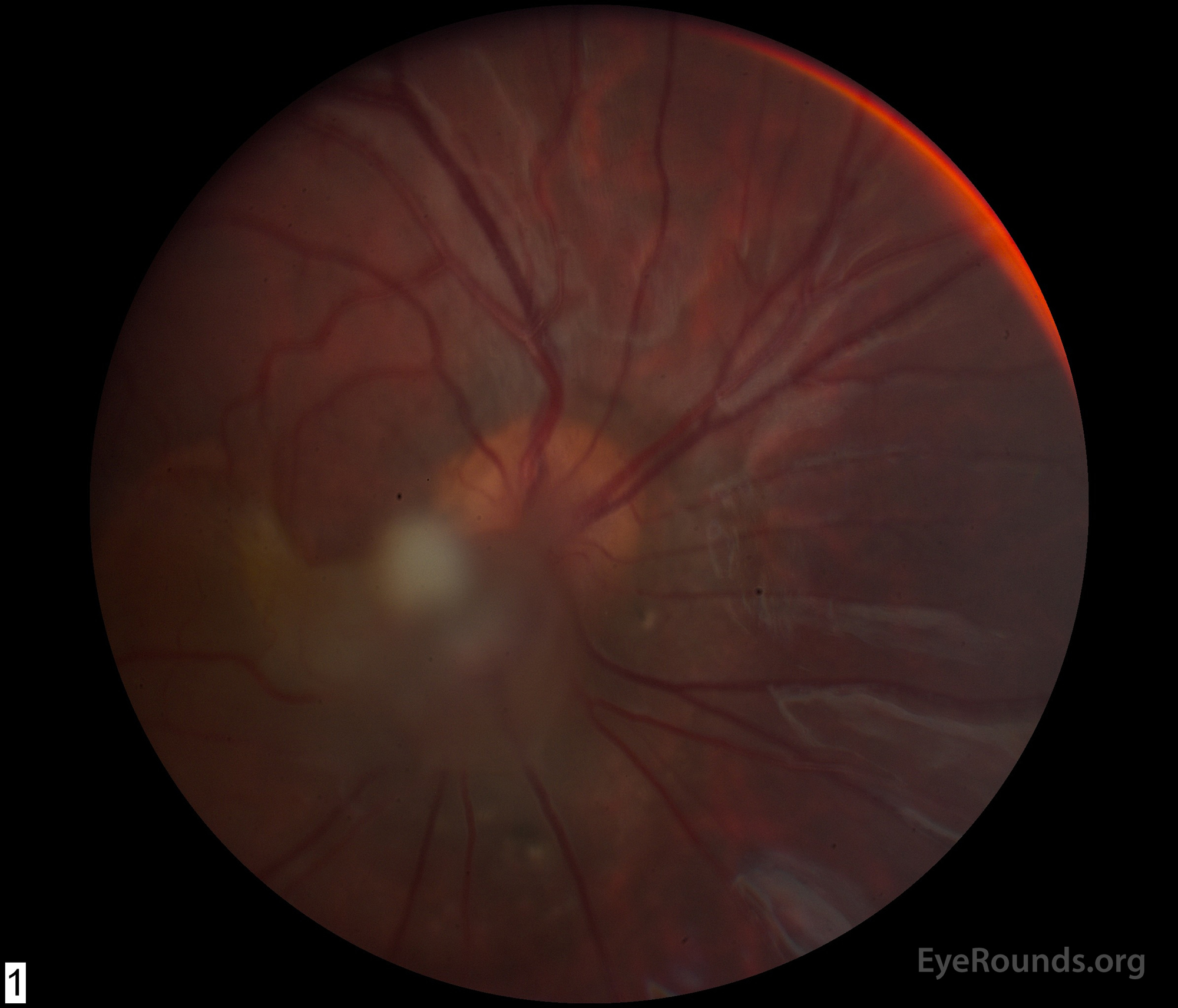
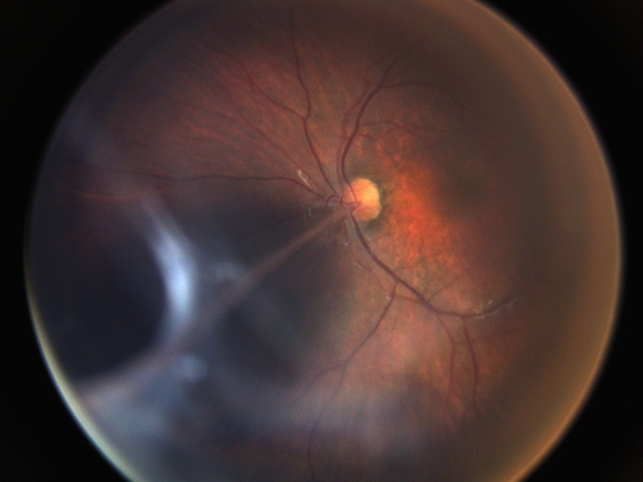
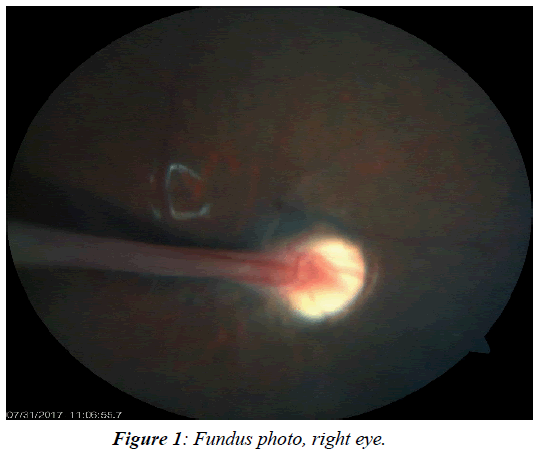
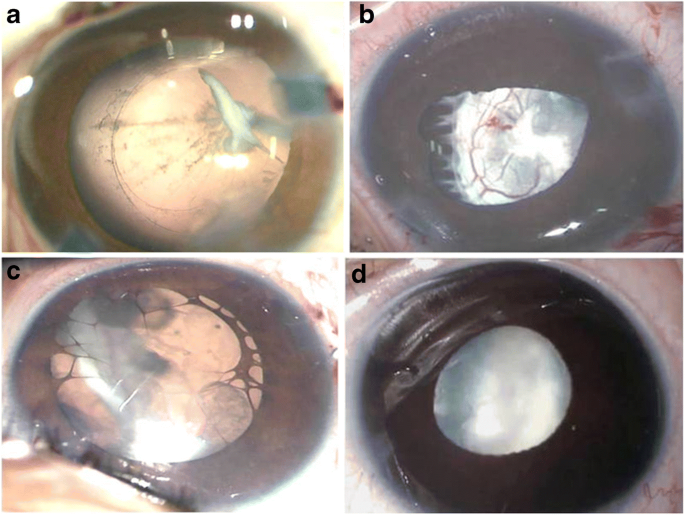
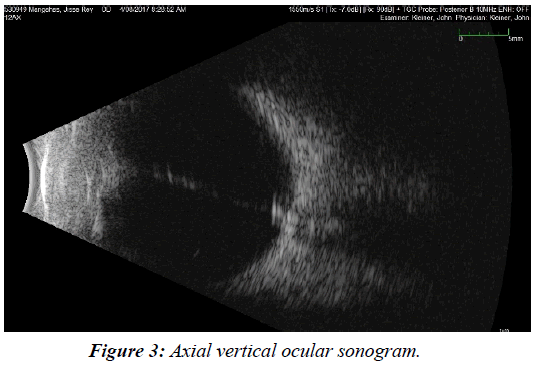
Persistent fetal vasculature previously known as persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous is a spectrum of disease and can present with no clinical effects or with severe morbidity. Persistent fetal vasculature PFV previously called persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous PHPV is a congenital defect that results when the fetal hyaloid vasculature fails to regress. FIGURE 532 Vessels extending from the.
1 We report the ocular and systemic findings as well as the management course of an infant who has all the characteristic features of PHACE syndrome and also describe what we believe to be the first reported case of this syndrome with Persistent Fetal. Persistent fetal vasculature PFV is a congenital developmental anomaly of the eye resulting from failure of the embryological primary vitreous and hyaloid vasculature to regress.
Persistent fetal vasculature previously known as persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous is a spectrum of disease and can present with no clinical effects or with severe morbidity.
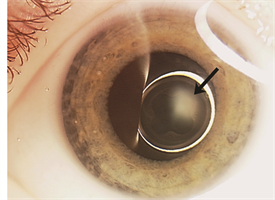
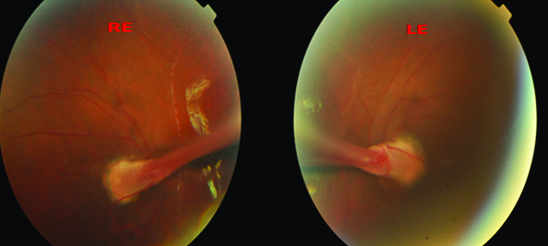
Persistent fetal vasculature PFV is a congenital developmental anomaly of the eye resulting from failure of the embryological primary vitreous and hyaloid vasculature to regress. Persistent fetal vasculature PFV previously called persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous PHPV is a congenital defect that results when the fetal hyaloid vasculature fails to regress. Genetic testing revealed a previously unreported mutation c1471AG pT491A in the gene ZNF408 which has been associated with autosomal recessive retinitis. This condition arises from failure of the hyaloid vasculature to undergo normal programmed involution. PHACE Syndrome is a neurocutaneous disease spectrum encompassing the following features. Persistent Fetal Vasculature Syndrome PFVS Usually PFVS is found in one eye that is somewhat smaller than the better eye and has a white pupil reflex and elongated ciliary processes. These vessels are persistent and not newly developed and therefore are best referred to as rubeosis iridis. In some eyes the stalk of persistent fetal vessels may not opacify the visual axis of the lens the part light rays pass through the. It is a condition that has to do with the way the eyes developed before the.
It is a condition that has to do with the way the eyes developed before the. MPPC syndrome has been described as a syndrome that presents with chorioretinal coloboma posterior megalolenticonus persistent fetal vasculature and chorioretinal coloboma. PHACE Syndrome is a neurocutaneous disease spectrum encompassing the following features. 1 We report the ocular and systemic findings as well as the management course of an infant who has all the characteristic features of PHACE syndrome and also describe what we believe to be the first reported case of this syndrome with Persistent Fetal. It can be either subtle no disturbance in vision or severe profound visual loss. Persistent Fetal Vasculature Syndrome PFVS Usually PFVS is found in one eye that is somewhat smaller than the better eye and has a white pupil reflex and elongated ciliary processes. Posterior fossa brain malformations large facial Hemangiomas Arterial anomalies Coarctation of the aorta and cardiac defects and Eye abnormalities.






















Post a Comment for "Persistent Fetal Vasculature Syndrome"